Accounting Assignment Help » Financial Accounting Assignment Help » Online Exam Help » Connect Principles of Financial Accounting Exam 1
Connect Principles of Financial Accounting Exam 1
Q1. The income statement describes revenues earned and expenses incurred along with the resulting net income or loss over a specified period of time, due to earnings activities. True or False
Q2. Objectivity means that financial information is supported by independent, unbiased evidence; it demands more than a person’s opinion. True or False
Q3. The idea that a business will continue to operate instead of being closed or sold underlies the going-concern assumption. True or False
Q4. The assets of a company total $728,000; the liabilities, $214,000. What are the net assets?
- $942,000
- $728,000
- $514,000
- $214,000
- It is impossible to determine unless the amount of stockholder investments is known
Q5. If the liabilities of a business increased $89,000 during a period of time and the equity in the business decreased $37,000 during the same period, the assets of the business must have:
- Decreased $126,000.
- Decreased $52,000.
- Increased $37,000.
- Increased $52,000.
- Increased $126,000.
Q6. The following financial statement information is from five separate companies:
| Company A | Company B | Company C | Company D | Company E | |
| December 31, 2016 | |||||
| Assets | $38,000 | $29,640 | $24,320 | $67,640 | $103,740 |
| Liabilities | 31,160 | 20,748 | 13,132 | 46,671 | ? |
| December 31, 2017 | |||||
| Assets | 41,000 | 29,520 | ? | 74,620 | 113,160 |
| Liabilities | ? | 20,073 | 13,460 | 35,817 | 89,396 |
| During year 2017 | |||||
| Stock issuance | 6,000 | 1,400 | 9,750 | ? | 6,500 |
| Net income (loss) | 9,110 | ? | (1,053) | 10,834 | 7,516 |
| Cash dividends | 3,500 | 2,000 | 5,875 | 0 | 11,000 |
2a. What is the amount of equity on December 31, 2016 for Company B.
2b. What is the amount of equity on December 31, 2017 for Company B
2c. What is net income for year 2017 for Company B.
Q7. Paul’s Landscaping paid $510 on account for supplies purchased in the prior month. Which of the following general journal entries will Paul’s Landscaping make to record this transaction?
- Debit Office supplies expense, $510; credit Cash, $510
- Debit Cash, $510; credit Office supplies, $510.
- Debit Office supplies, $510; credit Cash, $510.
- Debit Office supplies, $510; credit Accounts payable, $510.
- Debit Accounts payable, $510; credit Cash, $510.
Q8. Lu Lu’s Catering has a debt ratio equal to .3 and its competitor, Able’s Bakery, has a debt ratio equal to .7. Determine the statement below that is correct.
- Able’s Bakery has a smaller percentage of its assets financed with liabilities as compared to Lu Lu’s.
- Able’s Bakery’s financial leverage is less than Lu Lu’s.
- Able’s Bakery’s financial leverage is greater than Lu Lu’s
- Lu Lu’s has a higher risk from its financial leverage.
- Higher financial leverage involves lower risk.
Q9. A general journal is:
- A ledger in which amounts are posted from a balance column account.
- Not required if T-accounts are used.
- A complete record of all transactions in chronological order from which transaction amounts are posted to the ledger accounts.
- Not necessary in electronic accounting systems.
- A book of final entry because financial statements are prepared from it.
Q10. A debit is used to record which of the following:
- A decrease in an asset account.
- A decrease in an expense account.
- An increase in a revenue account.
- An increase in the common stock account.
- An increase in the dividends account.
Q11. Identify the statement below that is correct.
- The left side of a T-account is the credit side.
- Debits decrease asset and expense accounts, and increase liability, equity, and revenue accounts.
- The left side of a T-account is the debit side.
- Credits increase asset and expense accounts, and decrease liability, equity, and revenue accounts.
- In certain circumstances the total amount debited need not equal the total amount credited for a particular transaction.
Q12. The process of transferring general journal entry information to the ledger is called:
- Double-entry accounting.
- Posting.
- Balancing an account.
- Journalizing.
- Not required unless debits do not equal credits.
Q13. A column in journals and ledger accounts that is used to cross reference journal and ledger entries is the:
- Account balance column.
- Debit column.
- Posting reference column.
- Credit column.
- Description column.
Q14. The chronological record of each complete transaction that has occurred in a business is called the:
- Account balance.
- Ledger.
- Journal.
- Trial balance.
- Cash account.
Q15. Willow Rentals purchased office supplies on credit. The general journal entry made by Willow Rentals will include a:
- Debit to Accounts Payable.
- Debit to Accounts Receivable.
- Credit to Cash.
- Credit to Accounts Payable.
- Credit to Common Stock.
Q16. A business’s general journal provides a place for recording all of the following except:
- The transaction date.
- The names of the accounts involved.
- The amount of each debit and credit.
- An explanation of the transaction.
- The balance in each account.
Q17. An account balance is:
- The total of the credit side of the account.
- The total of the debit side of the account.
- The difference between the total debits and total credits for an account including the beginning balance
- Assets = liabilities + equity.
- Always a credit.
Q18. Identify the normal balance (debit or credit) for each of the following accounts.
- Rental Revenue – Credit
- Note Receivable – Debit
- Hair cutting Revenue – Debit
- Common Stock – Credit
- Prepaid Rent – Debit
- Dividends – Debit
- Salaries Payable – Credit
- Accounts Payable – Debit
- Prepaid Insurance – Debit
Q19. Identify whether a debit or credit results in the indicated change for each of the following accounts.
- To increase Prepaid Insurance – Debit
- To decrease Prepaid Rent – Credit
- To increase Utilities expenses – Debit
- To increase Consulting Revenue – Credit
- To decrease Unearned store sales – Debit
- To decrease office supplies – Credit
- To increase Unearned ticket revenue – Credit
- To decrease furniture – Credit
- To increase common stock – Credit
- To increase stock supplies – Debit
Q20. The adjusted trial balance contains information pertaining to:
- Asset accounts only.
- Balance sheet accounts only.
- Income statement accounts only.
- All general ledger accounts.
- Revenue accounts only.
Q21. On April 1, Griffith Publishing Company received $1,548 from Santa Fe, Inc. for 36-month subscriptions to several different magazines. The subscriptions started immediately. What is the amount of revenue that should be recorded by Griffith Publishing Company for the second year of the subscription assuming the company uses a calendar-year reporting period?
- $0
- $516
- $387
- $129
- $430
Q22. On July 1 of the current calendar year, Plum Co. paid $7,500 cash for management services to be performed over a two-year period beginning July 1. Plum follows a policy of recording all prepaid expenses to asset accounts at the time of cash payment. The adjusting entry on December 31 of the current year for Plum would include:
- A debit to an expense and a credit to a prepaid expense for $5,625.
- A debit to a prepaid expense and a credit to Cash for $5,625.
- A debit to an expense and a credit to a prepaid expense for $1,875.
- A debit to a prepaid expense and a credit to an expense for $1,875.
- A credit to a liability and a debit to a prepaid expense for $1,875.
Q23. The total amount of depreciation recorded against an asset over the entire time the asset has been owned:
- Is referred to as depreciation expense.
- Is referred to as accumulated depreciation.
- Is shown on the income statement of the final period.
- Is only recorded when the asset is disposed of.
- Is referred to as an accrued asset.
Q24. On January 1, Imlay Company purchases manufacturing equipment costing $95,000 that is expected to have a five-year life and an estimated salvage value of $5,000. Imlay uses the straight-line depreciation method to allocate costs, and only prepares adjustments at year-end. The adjusting entry needed on December 31 of the first year is:
- Debit Depreciation Expense, $9,000; credit Accumulated Depreciation, $9,000.
- Debit Depreciation Expense, $18,000; credit Accumulated Depreciation, $18,000.
- Debit Depreciation Expense, $90,000; credit Accumulated Depreciation, $90,000.
- Debit Depreciation Expense, $18,000; credit Equipment, $18,000.
- Debit Depreciation Expense, $9,000; credit Equipment, $9,000.
Q25. The following information is available for the Noir Detective Agency. After closing entries are posted, what will be the balance in the Retained earnings account?
| Net Loss | $17,600 |
| Retained earnings | 289,000 |
| Dividends | 32,000 |
- $239,400
- $274,600
- $303,400
- $289,000
- $257,000
Q26. A company purchased $1,800 of merchandise on July 5 with terms 2/10, n/30. On July 7, it returned $200 worth of merchandise. On July 28, it paid the full amount due. Assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and records purchases using the gross method, the correct journal entry to record the merchandise return on July 7 is:
- Debit Merchandise Inventory $1,600; credit Cash $1,600.
- Debit Merchandise Inventory $200; credit Accounts Payable $200.
- Debit Merchandise Inventory $200; credit Sales Returns $200.
- Debit Accounts Payable $200; credit Merchandise Inventory $200.
- Debit Accounts Payable $1,800; credit Purchase Returns $200; credit Merchandise Inventory $1,600.
Q27. When preparing an unadjusted trial balance using a periodic inventory system, the amount shown for Merchandise Inventory is:
- The ending inventory amount.
- The beginning inventory amount.
- Equal to the cost of goods sold.
- Equal to the cost of goods purchased.
- Equal to the gross profit.
Q28. The operating cycle for a merchandiser that sells only for cash moves from:
- Purchases of merchandise to inventory to cash sales.
- Purchases of merchandise to inventory to accounts receivable to cash sales.
- Inventory to purchases of merchandise to cash sales.
- Accounts receivable to purchases of merchandise to inventory to cash sales.
- Accounts receivable to inventory to cash sales.
Q29. A company’s gross profit was $83,750 and its net sales were $347,800. Its gross margin ratio equals:
- 4.2%
- 24.1%
- 75.9%
- $83,750
- $264,050
Q30. A debit memorandum is:
- Required whenever a journal entry is recorded.
- The source document for the purchase of merchandise inventory.
- Required when a purchase discount is granted.
- The document a buyer issues to inform the seller of a debit made to the seller’s account payable in the buyer’s records.
- Not necessary in a perpetual inventory system.
Q31. Expenses that support the overall operations of a business and include the expenses relating to accounting, human resource management, and financial management are called:
- Cost of goods sold.
- Selling expenses.
- Purchasing expenses.
- General and administrative expenses.
- Non-operating activities.
Q32. During a period of steadily rising costs, the inventory valuation method that yields the highest reported net income is:
- Specific identification method.
- Average cost method.
- Weighted-average method.
- FIFO method.
- LIFO method.
Q33. Use the following information for Davis Company to compute inventory turnover for Year 2.
| Year 2 | Year 1 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 279,500 | 291,800 |
| Ending inventory | 47,700 | 49,350 |
- 5.86
- 5.76
- 5.67
- 11.77
- 5.89
Q34. Maintaining adequate records is an important internal control principle. True or False
Q35. Basic bank services such as bank accounts, bank deposits, and checking contribute to the control of cash. True or False
Q36. Cash registers, time clocks, and personal identification scanners are examples of technologies that can improve internal control. True or False
Q37. Most large thefts occur from payment of fictitious invoices, which makes control of cash disbursements especially important for companies. True or False
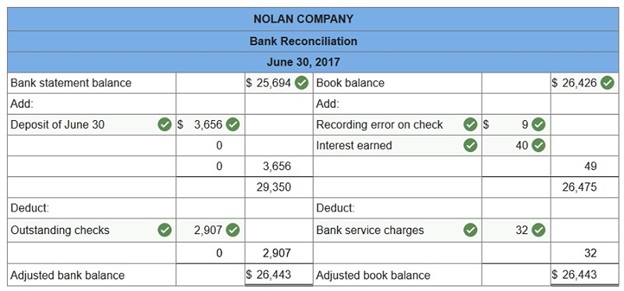
Q38. Nolan Company deposits all cash receipts on the day when they are received and it makes all cash payments by check. At the close of business on June 30, 2017, its Cash account shows a $26,426 debit balance. Nolan’s June 30 bank statement shows $25,694 on deposit in the bank.
- Outstanding checks as of June 30 total $2,907.
- The June 30 bank statement included a $32 debit memorandum for bank services; the company has not yet recorded the cost of these services.
- In reviewing the bank statement, a $80 check written by the company was mistakenly recorded in the company’s books at $89.
- June 30 cash receipts of $3,656 were placed in the bank’s night depository after banking hours and were not recorded on the June 30 bank statement.
- The bank statement included a $40 credit for interest earned on the cash in the bank.
Prepare a bank reconciliation for Nolan Company using the above information.