Principles of Microeconomics Exam 1 Answers
Q1. The opportunity cost to free trade is
- greater efficiency.
- government involvement
- domestic jobs
- lower prices
- economic growth
Q2. What creates comparative advantage?
- lower costs
- higher opportunity costs
- specialization
- scarcity
- population growth
Q3. An example of a direct negative incentive is
- providing an orientation for new employees
- providing a commission for sales
- providing generous benefits and pay for employees
- threatening to fire those who do not perform well
- awarding a promotion for hard work
Q4. Which of the following is a normative statement?
- On average, people save 15 percent when they switch to GEICO
- In January, the average temperature in Fargo, North Dakota, is 56 degrees
- The current exchange rate is 0.7 British pounds per U.S. dollar
- University of Virginia graduates earn more than Duke University graduates
- Winters in Arkansas are too cold
Q5. Which of the following is a positive statement?
- On average, people save 15 percent when they switch to GEICO
- Everyone should work in a bank to understand the true value of money
- Harvard University is the top education institution in the country
- Winters in Arkansas are too cold
- Everyone ought to have a life insurance policy
Q6. Refer to the following figure to answer the following questions.
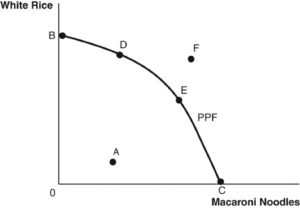
What is the most preferred consumption point for a carbohydrate-loving society?
- Point E
- Point B
- Point C
- Point F
- Point D
Q7. For a firm to have market power, it must
- have some control over price
- be a monopoly
- be the sole producer of a product
- rely on the government to protect its price
Q8. Which of the following firms participates in a competitive market?
- A corn farmer at a farmer’s market
- A new car manufacturer, such as Ford, Honda, Toyota, or GMC
- A software producer, such as Microsoft
- A local electric utility company
Q9. Suppose that Coca Cola and Pepsi are substitutes in consumption. If the price of Coca Cola decreases, then which of the following graphs would be relevant for Pepsi?
- Graph A
- Graph B
- Graph C
- Graph D
Q10. Refer to the following figure. At a price of $5, this market is experiencing
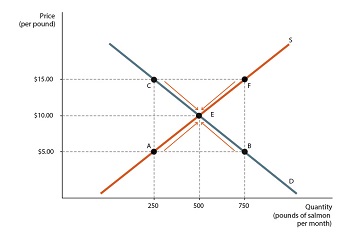
- a surplus
- equilibrium
- a shortage
- None of the other options are correct
Q11. In a competitive market, the price of the product is
- independently set by each competing seller
- set by the market leader and then copied by other sellers
- set by market supply and demand
- jointly set after a meeting of all sellers in the market
Q12. Price elasticity of demand measures the change in
- price due to the change in demand
- quantity demanded due to the change in price
- demand due to the change in price
- price due to a change in quantity demanded
- quantity demanded due to the change in price of another good or service
Q13. When incomes fall by 20 percent, quantity demanded of specialty baked goods falls by 50 percent. Specialty baked goods are
- luxuries
- complements to butter
- necessities
- inferior goods
- substitutes for mass-produced bread
Q14. If the price elasticity of demand is − 4.0, a 5 percent decrease in price will increase quantity demanded by
- 20 percent
- 0.8 percent
- 1.25 percent
- 125 percent
- 80 percent
Q15. If the income elasticity of demand is 1.2, the good will be a(n) ________ good
- substitute
- complement
- inferior
- necessity
- luxury
Q16. Deadweight loss is defined as
- who pays a tax out of pocket
- the benefit from additional government spending
- the cost to society created by distortions in the market
- how much revenue a tax generates
- the dollar cost of a tax per unit of sale
Q17. When demand is perfectly inelastic, the demand curve is
- U-shaped
- vertical
- upward sloping
- horizontal
- downward sloping
Q18. Producer surplus is depicted by the area
- above market price and below the supply curve
- above market price and below the demand curve
- below market price and above the supply curve
- between the supply curve and the demand curve
- above the demand curve and below the supply curve
Q19. Refer to the accompanying table to answer the following questions.
| Monthly Rent | Quantity of Apartments Demanded |
Quantity of Apartments Supplied |
| $1,500 | 136,500 | 78,100 |
| $1,550 | 112,750 | 83,760 |
| $1,600 | 107,000 | 87,900 |
| $1,650 | 100,100 | 94,250 |
| $1,700 | 98,450 | 98,450 |
| $1,750 | 95,000 | 118,500 |
| $1,800 | 92,800 | 125,600 |
At what price level does the apartment market experience its largest surplus?
- $1,750
- $1,700
- $1,550
- $1,800
- $1,500
Q20. Use the following information to answer the following questions.
Market for used cars:
Demand: Qd = 154,000 – 86P Supply: Qs = –100 + 14P
What would be the quantity supplied if a price ceiling is set at $2,000?
- 21,474
- 27,900
- 100
- 18,000
- 154,100
Q21. The long-run effects of rent control support one of the five foundations of economics, namely, that
- society faces a trade-off between homelessness and rent control
- one must give up something in order to get something else
- social planners must think marginally in allocating housing
- exchange makes everyone better off.
- people respond to incentives
Q22. Do all sellers benefit from a binding price floor?
- Yes. A binding price floor benefits all sellers because it allows all sellers to sell as much as they produce on the legal market
- No. A binding price floor doesn’t benefit any sellers because sellers will be unwilling to sell any of their products
- No. A binding price floor doesn’t benefit any buyers because buyers are unwilling to purchase any of the products at a price lower than the equilibrium
- No. A binding price floor benefits only some sellers because not all are able to sell as much as they would like in the legal market
- No. A binding price floor benefits only some sellers because the price is initially higher but then eventually decreases to the equilibrium price
Q23. Negative externalities have ________ for third parties
- social costs
- internal costs
- internal benefits
- external benefits
- external costs
Q24. In the graph below, Q2 is the market equilibrium of output of this product, and Q1 is the social optimum. The graph below shows a __________ externality, which can be corrected to the optimal level with a ______________.
- negative, tax
- positive, tax
- positive, subsidy
- negative, subsidy
Q25. Which of the following is a club good?
- streetlights
- a Fourth of July fireworks show
- a bacon double cheeseburger
- a swimming pool
Q26. Which one of the following is an example of perfectly competitive market?
- shoes
- T-shirts
- Soft drinks
- Bananas
Q27. In the circular-flow diagram, firms
- Purchase good and services
- Demand factors of productions
- Are the only decision makers
- Own the factors of productions
Q28. Production Possibilities for FootLocker
| Shoes | Socks |
| 800 | 0 |
| 600 | 400 |
| 400 | 700 |
| 200 | 900 |
| 0 | 1000 |
What is the opportunity cost to Footlocker of increase the production of shoes from 400 to 800?
- 100 socks
- 700 socks
- 200 socks
- 400 socks
Q29. Assume that England and Spain can switch between producing cheese and producing bread at a constant rate.
| Labor Hours Needed to Make 1 Unit of | Number of Units Produced in 24 Hours | |||
| Cheese | Bread | Cheese | Bread | |
| England | 2 | 3 | 12 | 8 |
| Spain | 3 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
Which of the following statement is correct?
- Spain has the absolute advantage in both cheese and bread
- England has the absolute advantage in both cheese and bread
- England has comparative advantage in both cheese and bread
- Spain has the comparative advantage in both cheese and bread
Q30. Absolute advantage is found by comparing different producers’
- Location and logistical circumstance
- Payments to resources
- Opportunity costs
- Input requirement per unit of output
Q31. Suppose the cost of driving a 50 seat bus is $1000 and there are 10 empty seats on a bus. The marginal cost of one additional passenger is
- $25
- $0
- $50
- $20
Q32. Assume that England and Spain can switch between producing cheese and producing bread at a constant rate.
| Labor Hours Needed to Make 1 Unit of | Number of Units Produced in 24 Hours | |||
| Cheese | Bread | Cheese | Bread | |
| England | 2 | 3 | 12 | 8 |
| Spain | 3 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
What’s the opportunity cost of cheese in Spain
- 1/2 bread
- 6 hours of labor
- 3 hours of labor
- 2 bread
Q33. A movement downward and to the right along the demand curve is called
- Increase in demand
- Decrease in quantity demanded
- Increase in quantity demanded
- Decrease in demand
Q34. Refer to the figure, which arrow represents the flow of income payments?
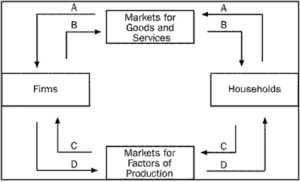
- A
- C
- D
- B
Q35. Which one of the following is an example of perfectly competitive market?
- fast foods
- computers
- printer papers
- automobiles
Q36. Consider Jason’s decision to go to college. If he goes to college, he will spend $25,000 on tuition, $10,000 on room ad board, and $3,000 on books. If he does not go to college, he will earn $22,000 working in a store and spend $9,000 on room and board. Jason’s cost of going to college is
- $69,000
- $38,000
- $60,000
- $51,000
Q37. Assume that England and Spain can switch between producing cheese and producing bread at a constant rate.
| Labor Hours Needed to Make 1 Unit of | Number of Units Produced in 24 Hours | |||
| Cheese | Bread | Cheese | Bread | |
| England | 2 | 3 | 12 | 8 |
| Spain | 3 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
If both country decide to specialize in the good they have the comparative advantage in, what is the combine production between the two countries?
- 12 cheese and 8 bread
- 3 cheese and 3 bread
- 8 cheese and 8 bread
- 12 cheese and 4 bread
Q38. What do points on the PPF represent?
- unattainable
- impossible
- efficient
- inefficient
Q39. Which one of the following is not part of the factors of production?
- money
- land
- capital
- labor
Q40. If the income increase lead to demand increase, this implies that the good is
- normal goods
- substitute goods
- complementary goods
- inferior goods
Q41. What is opportunity cost of an item?
- What you must give up to get that item
- Total dollar cost of purchase before tax
- The amount of time that associated with earning the income to buy the good
- Total dollar cost of purchase after tax
Q42. Rational decision makers make their decision based on comparing?
- Total costs and total benefits
- Average costs and average benefits
- Opportunity costs and opportunity benefits
- Marginal costs and marginal benefits
Q43. Competitive market is a market in which
- Both buyers and sellers have substantial market power
- None of the above
- There is only one buyer
- There is only one seller
Q44. Which point represent an impossible production combination?
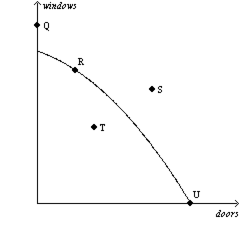
- U
- Q
- T
- R
Q45. At which point is the economy producing inefficiently?
- T
- Q
- S
- R
Q46. Suppose the cost of driving a 20 seat bus is $500 and there are 5 empty seats on a bus. The marginal cost of one additional passenger is
- $500
- $25
- $33.33
- $0
Q47. Consider Jerry’s decision to go to college. If he goes to college, he will spend $15,000 on tuition, $12,000 on room ad board, and $2,000 on books. If he does not go to college, he will earn $27,000 working in a store and spend $10,000 on room and board. Jerry’s cost of going to college is
- $56,000
- $46,000
- $66,000
- $29,000
Q48. What is the opportunity cost moving from point A to B?
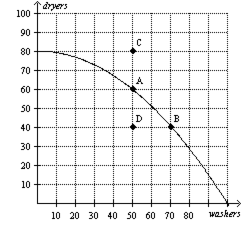
- 40 dryers
- 20 dryers
- 20 washers
- 50 washers
Q49. What do points outside of the production possibility curve represent?
- impossible
- possible
- efficient
- inefficient
Q50. At which point is the economy producing the maximum number of windows?
- U
- S
- T
- R
