Urgent Assignment Help » Accounting Assignment Help » Financial Accounting Assignment Help » Connect Financial Accounting Chapter 7
Connect Financial Accounting Chapter 7
Q1. Vail Company recorded the following selected transactions during November Current Year.
| Date | General Journal | Debit | Credit |
| Nov 5 | Accounts Receivable—Ski Shop | 4,182 | |
| Sales | 4,182 | ||
| Nov 10 | Accounts Receivable—Welcome Enterprises | 2,749 | |
| Sales | 2,749 | ||
| Nov 13 | Accounts Receivable—Zia Natara | 1,612 | |
| Sales | 1,612 | ||
| Nov 21 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 416 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Zia Natara | 416 | ||
| Nov 30 | Accounts Receivable—Ski Shop | 5,731 | |
| Sales | 5,731 |
1. Prepare a general ledger having T-accounts for Accounts Receivable, Sales, and Sales Returns and Allowances. Post these entries to both the general ledger and the accounts receivable ledger.
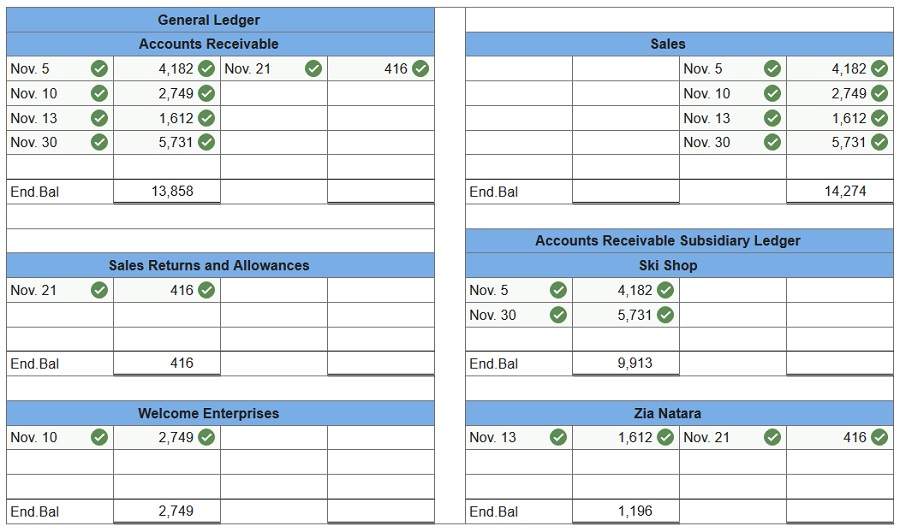
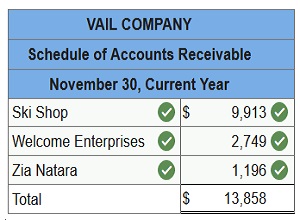
2. Prepare a schedule of accounts receivable.
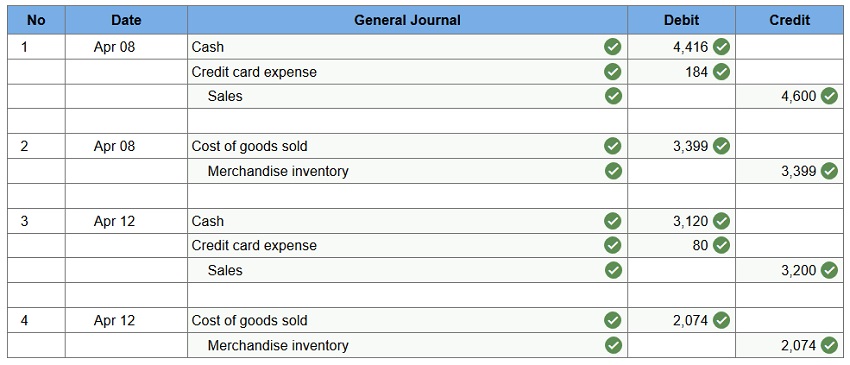
Q2. Levine Company uses the perpetual inventory system and allows customers to use two credit cards in charging purchases. With the Suntrust Bank Card, a 4% service charge for credit card sales is assessed. The second credit card that Levine accepts is the Continental Card. Continental assesses a 2.5% charge on sales for using its card.
- Apr 8 – Sold merchandise for $4,600 (that had cost $3,399) and accepted the customer’s Suntrust Bank Card.
- Apr 12 – Sold merchandise for $3,200 (that had cost $2,074) and accepted the customer’s Continental Card.
Prepare journal entries to record the above selected credit card transactions of Levine Company. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
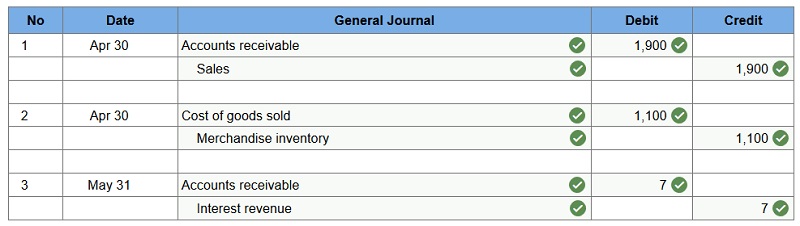
Q3. Z-Mart uses the perpetual inventory system and allows customers to use the Z-Mart store credit card in charging purchases. Z-Mart assesses a per-month interest fee for any unpaid balance on its store credit card at each month-end.
- Apr 30 – Z-Mart sold merchandise for $1,900 (that had cost $1,100) and accepted the customer’s Z-Mart store credit card.
- May 31 – Z-Mart recorded $7 of interest earned from its store credit card as of this month-end.
Prepare journal entries to record the above selected credit card transactions of Z-Mart.
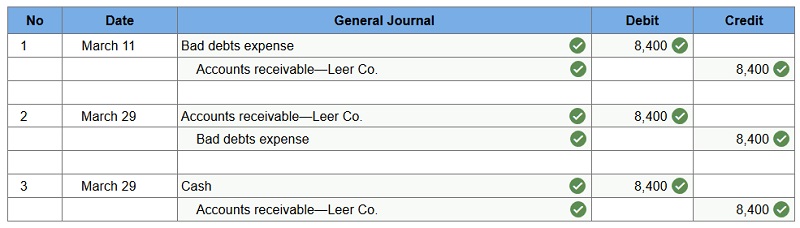
Q4. Dexter Company applies the direct write-off method in accounting for uncollectible accounts.
- March 11 – Dexter determines that it cannot collect $8,400 of its accounts receivable from its customer Leer Company.
- March 29 – Leer Company unexpectedly pays its account in full to Dexter Company. Dexter records its recovery of this bad debt.
Prepare journal entries to record the above selected transactions of Dexter.
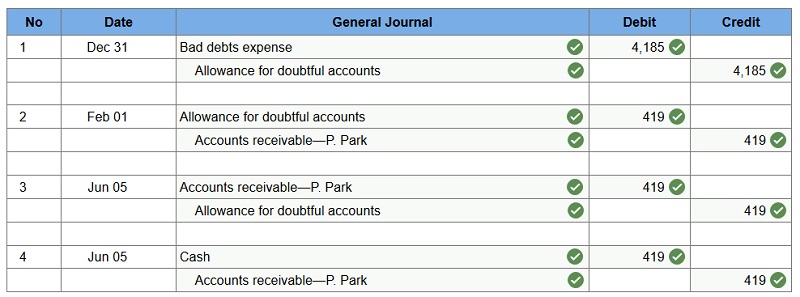
Q5. At year-end (December 31), Chan Company estimates its bad debts as 0.50% of its annual credit sales of $837,000. Chan records its Bad Debts Expense for that estimate. On the following February 1, Chan decides that the $419 account of P. Park is uncollectible and writes it off as a bad debt. On June 5, Park unexpectedly pays the amount previously written off.
Prepare the journal entries for these transactions.
Connect Financial Accounting Chapter 7 Quiz
Q1. On July 9, Mifflin Company receives an $8,500, 90-day, 8% note from customer Payton Summers as payment on account. Compute the amount due at maturity for the note. (Use 360 days a year.)
- $8,628
- $8,192
- $8,613
- $8,500
- $8,670
Q2. A company has net sales of $1,200,000 and average accounts receivable of $400,000. What is its accounts receivable turnover for the period?
- 0.33
- 5.00
- 20.0
- 73.0
- 3.0
Q3. Under IFRS, the term provision:
- Refers to expense
- Usually refers to a liability whose amount or timing is uncertain.
- Means establishing a provision for bad debts.
- Means establishing a contra-asset account.
- Means establishing an asset account.
Q4. Kenai Company sold $600 of merchandise to a customer who used a National Bank credit card. National Bank deducts a 3% service charge for sales on its credit cards. Kenai electronically remits the credit card sales receipts to the credit card company and receives payment immediately. The journal entry to record the collection from the credit card company would be:
- Debit Cash of $618 and credit Accounts Receivable—National $618.
- Debit Cash of $618; credit Credit Card Expense $18 and credit Sales $600.
- Debit Accounts Receivable—National $582; debit Credit Card Expense $18 and credit Sales $600.
- Debit Cash $582; debit Credit Card Expense $18 and credit Sales $600.
- Debit Cash $582 and credit Sales $582.
Q5. Giorgio Italian Market bought $4,000 worth of merchandise from Food Suppliers and signed a 90-day, 6% promissory note for the $4,000. Food Supplier’s journal entry to record the collection on the maturity date is: (Use 360 days a year.)
- Debit Cash $4,060; credit Notes Receivable $4,060
- Debit Notes Receivable $4,000; credit Cash $4,000
- Debit Cash $4,000; debit Interest Receivable $60; credit Sales $4,060
- Debit Notes Receivable $4,060; credit Sales $4,060
- Debit Cash $4,060; credit Interest Revenue $60; credit Notes Receivable $4,000
Q6. Jervis accepts all major bank credit cards, including those issued by Northern Bank (NB), which assesses a 3% charge on sales for using its card. On June 28, Jervis had $3,500 in NB Card credit sales. What entry should Jervis make on June 28 to record the deposit?
- Debit Cash $3,500; credit Sales $3,500
- Debit Accounts Receivable $3,500; credit Sales $3,500
- Debit Cash $3,605; credit Credit Card Expense $105; credit Sales $3,500
- Debit Cash $3,395; debit Credit Card Expense $105; credit Sales $3,500
- Debit Accounts Receivable $3,395; debit Credit Card Expense $105; credit Sales $3,500
Q7. Jasper makes a $25,000, 90-day, 7% cash loan to Clayborn Co. Jasper’s entry to record the collection of the note and interest at maturity should be: (Use 360 days a year.)
- Debit Cash for $25,000; credit Notes Receivable $25,000.
- Debit Cash $25,437.50; credit Interest Revenue $437.50; credit Notes Receivable $25,000.
- Debit Cash $25,437.50; credit Notes Receivable for $25,437.50.
- Debit Notes Payable $25,000; Debit Interest Expense $1,750; credit Cash $26,750.
- Debit Cash $26,750; credit Interest Revenue $1,750, credit Notes Receivable $25,000.
Q8. Valley Spa purchased $7,800 in plumbing components from Tubman Co. Valley Spa signed a 60-day, 10% promissory note for $7,800. If the note is dishonored, but Tubman intends to continue collection efforts, what is the journal entry to record the dishonored note? (Use 360 days a year.)
- Debit Accounts Receivable $7,930; debit Bad Debt Expense $130; credit Notes Receivable $8,060.
- Debit Bad Debt Expense $7,930; credit Accounts Receivable $7,930.
- Debit Bad Debt Expense $7,800; credit Notes Receivable $7,800.
- Debit Accounts Receivable—Valley Spa $7,800; credit Notes Receivable $7,800.
- Debit Accounts Receivable—Valley Spa $7,930, credit Interest Revenue $130; credit Notes Receivable $7,800.
Q9. MacKenzie Company sold $180 of merchandise to a customer who used a Regional Bank credit card. Regional Bank deducts a 4% service charge for sales on its credit cards. MacKenzie electronically remits the credit card sales receipts to the credit card company and receives payment immediately. The journal entry to record this sale transaction would be:
- Debit Cash of $180 and credit Sales $180.
- Debit Cash of $180 and credit Accounts Receivable—Regional $180.
- Debit Accounts Receivable—Regional $172.80; debit Credit Card Expense $7.20 and credit Sales $180.
- Debit Cash $172.80; debit Credit Card Expense $7.20 and credit Sales $180.
- Debit Cash $172.80 and credit Sales $172.80.
If the digits in your course is different, you can connect with us via live chat or you can submit your assignment details using the Submit Requirements form given in the right sidebar. We will get back to you soon.
